The Amaziğ people, often referred to as the Berbers, are an indigenous community deeply rooted in the landscapes of North Africa. Their narrative traces back to ancient times, where they’re believed to be the original inhabitants of the region, fostering a legacy that spans millennia.
The essence of “Amaziğ” encapsulates the spirit of freedom and nobility, resonating through the Tamazight language they speak. Within this linguistic tapestry lie nuances that define their identity, reflecting a cultural richness that sets them apart. From the rugged Atlas Mountains to the sun-kissed sands of the Sahara, the Amaziğ people weave a vibrant tapestry of traditions, dialects, and customs, each thread contributing to a unique mosaic of North African heritage.
In the bustling medinas of Morocco to the remote villages nestled in the Atlas foothills, the spirit of the Amaziğ endures, echoing through time. Their resilience and reverence for the land are evident in rituals, storytelling, and celebrations that honor their past while embracing the present. As guardians of an ancient legacy, the Amaziğ people continue to thrive, their cultural tapestry serving as a testament to the enduring spirit of North Africa’s indigenous inhabitants.
What Does ‘Amaziğ’ Truly Signify?

The term “Amaziğ,” often synonymous with the Berber people, carries profound significance within the context of North African history and society. These indigenous communities boast a heritage that stretches back countless generations, weaving a rich tapestry of languages, traditions, and narratives that have shaped the region’s cultural landscape. From the rugged Atlas Mountains to the sun-soaked Sahara, the Amaziğ people have cultivated a diverse array of customs and stories, each thread contributing to the intricate fabric of their identity.
The word “Amaziğ” itself serves as a reflection of this deep-rooted heritage, resonating with layers of cultural richness and resilience. It embodies not only a linguistic marker but also a testament to the enduring spirit of a people who have navigated the complexities of history with grace and determination. Through their languages, traditions, and stories, the Amaziğ community continues to uphold and celebrate their unique identity, offering a glimpse into the vibrant mosaic of North African heritage.
Origins Of The Amaziğ People
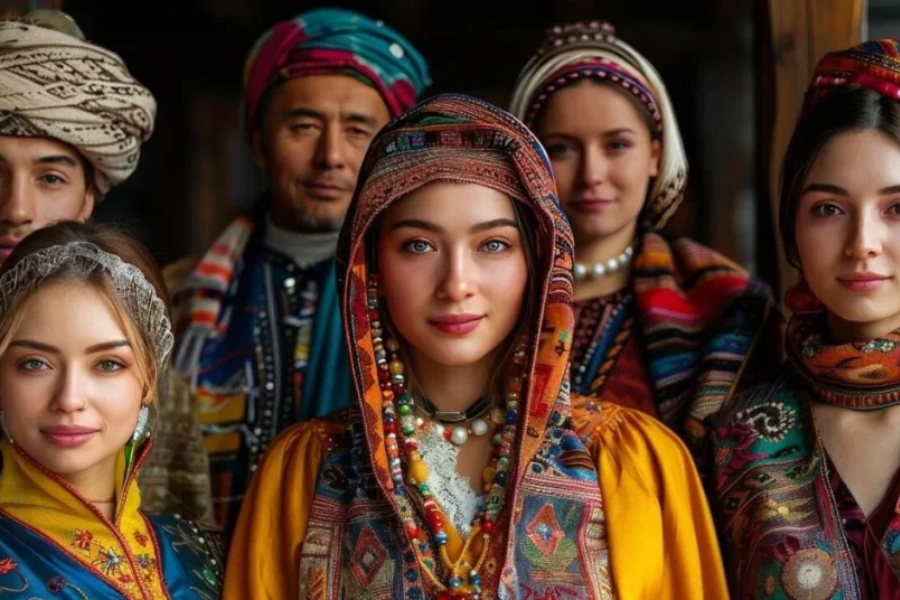

The Amaziğ people’s origins unfurl like an ancient scroll, revealing a narrative woven through the tapestry of time itself. Their presence in North Africa stretches back to the dawn of civilization, their roots buried deep in the soil of antiquity. Through the ages, they have weathered the storms of history, their story marked by resilience and adaptation.
Since time immemorial, the Amaziğ have inhabited the rugged terrain of North Africa, their footsteps echoing across the sands of time. Despite the tides of change brought by waves of migration and conquest, they have remained guardians of their ancestral homelands. Amidst the rise and fall of empires, from the Phoenicians to the Romans, Arabs, and Europeans, the Amaziğ people have endured, preserving their language, traditions, and customs as a testament to their enduring spirit.
Embedded within the fabric of their culture lies a rich tapestry of diversity, shaped by centuries of interaction with neighboring civilizations. Their story is one of resilience, adaptation, and cultural vibrancy, a testament to the enduring legacy of North Africa’s indigenous peoples. Today, as guardians of an ancient heritage, the Amaziğ people continue to carve their path through history, their story serving as a bridge between the past and the present, a testament to the enduring power of human resilience and identity.
Who Does The Amaziğ Look Like?
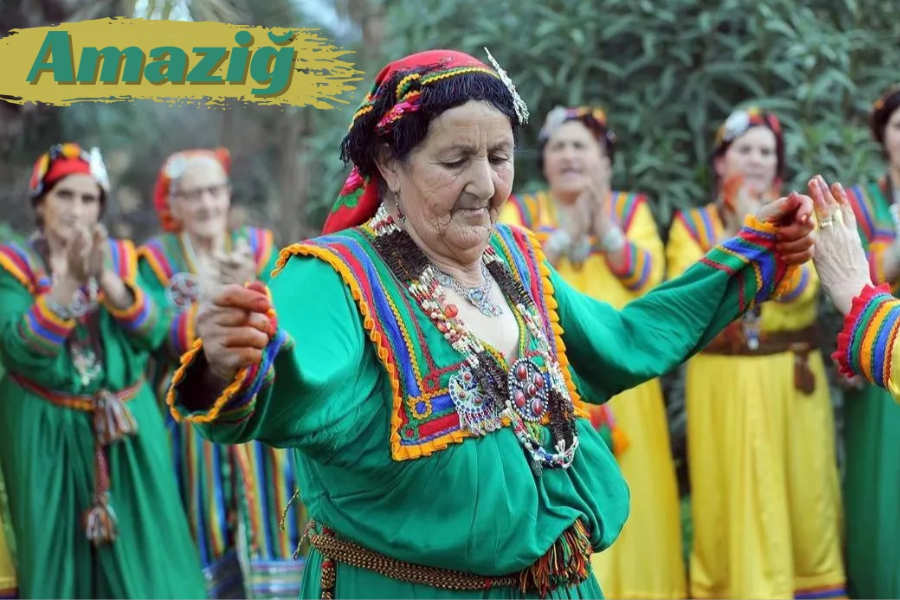

The Amaziğ, also known as the Berbers, comprise a diverse group of individuals whose ancestry spans generations in North Africa. Like any community, they exhibit a broad spectrum of physical traits reflective of their rich heritage. From varying skin tones to different hair textures and facial features, the Amaziğ people embody the diversity inherent in human populations.
While certain physical characteristics may hint at shared ancestry within the broader racial classification, the Amaziğ community encompasses a mosaic of traits that defy simple categorization. Their unique blend of features serves as a testament to the complex interplay of genetic influences and cultural exchange that have shaped their identity over time.
Ultimately, the Amaziğ people, like all human groups, are united by their shared history, culture, and sense of belonging, transcending superficial distinctions to celebrate the rich tapestry of human diversity.
Amaziğ People Language And Culture

The language and culture of the Amaziğ people paint a vivid picture of their rich heritage and identity. Known as Tamaziğt or Berber, their language is a mosaic of closely connected dialects spoken by diverse communities across North Africa. This linguistic diversity reflects the myriad landscapes and histories that have shaped the Amaziğ people over centuries.
Within the tapestry of Amaziğ languages, each dialect carries the echoes of its unique regional influences, yet they are bound together by common linguistic features and cultural traditions. These shared elements serve as the threads weaving the fabric of Amaziğ identity, fostering a sense of unity and belonging among its people.
Beyond language, the cultural landscape of the Amaziğs is a vibrant tapestry adorned with the colors of music, dance, art, cuisine, and ceremonial rituals. These traditions passed down through generations, not only celebrate the richness of Amaziğ heritage but also serve as a beacon guiding the community through the currents of time. As guardians of their culture, the Amaziğ people continue to nurture and preserve these traditions, ensuring that their identity remains rooted in the fertile soil of their collective past.
Cultural And Artistic Contributions
The Amaziğ people have made significant contributions to the cultural and artistic landscape of North Africa and beyond. Their influence can be observed in various forms of artistic expression, including literature, architecture, and visual arts.
Sustainable Living Practices
The Amaziğ people have developed sustainable living practices rooted in their deep connection to the land and environment. These practices encompass traditional agriculture techniques, water management systems, and conservation methods aimed at preserving natural resources and fostering harmony with nature.
Family And Community Bonds
The Amaziğ society revolves around the nucleus of the family unit, where strong kinship ties and communal solidarity form the foundation of daily life. Within tightly-knit communities, members share a sense of responsibility towards one another, fostering a deep sense of belonging and support.
1. Evolution of Gender Roles
Amaziğ societal norms navigate a delicate balance between tradition and modernity, particularly concerning gender roles. As cultural paradigms shift and socio-economic dynamics evolve, so too do perceptions and expectations surrounding the roles of men and women within the community.
2. Cultural Identity Through Attire
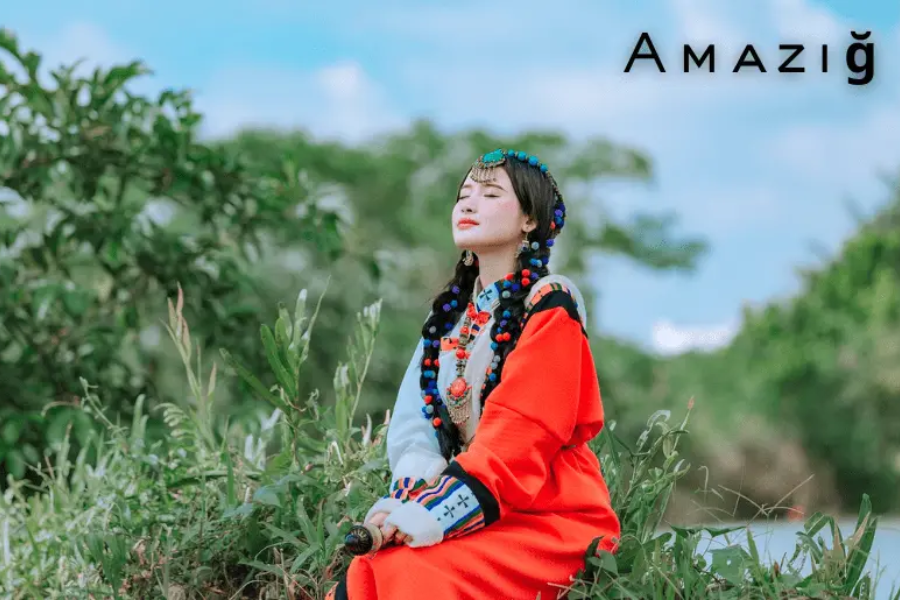
The traditional clothing of the Amaziğ people serves as more than mere fabric; it is a visual representation of their cultural identity and heritage. Adorned with intricate patterns, vibrant colors, and symbolic motifs, each garment tells a story, weaving together threads of tradition and history.
3. A Gastronomic Journey
Embark on a culinary adventure through the rich tapestry of Amaziğ culinary traditions. From aromatic spices to hearty stews and savory pastries, each dish offers a tantalizing glimpse into their culinary heritage. Nourishing both body and soul, these culinary delights reflect the diverse flavors and influences that have shaped Amaziğ cuisine over generations.
Artistic Expression In Amaziğ Culture
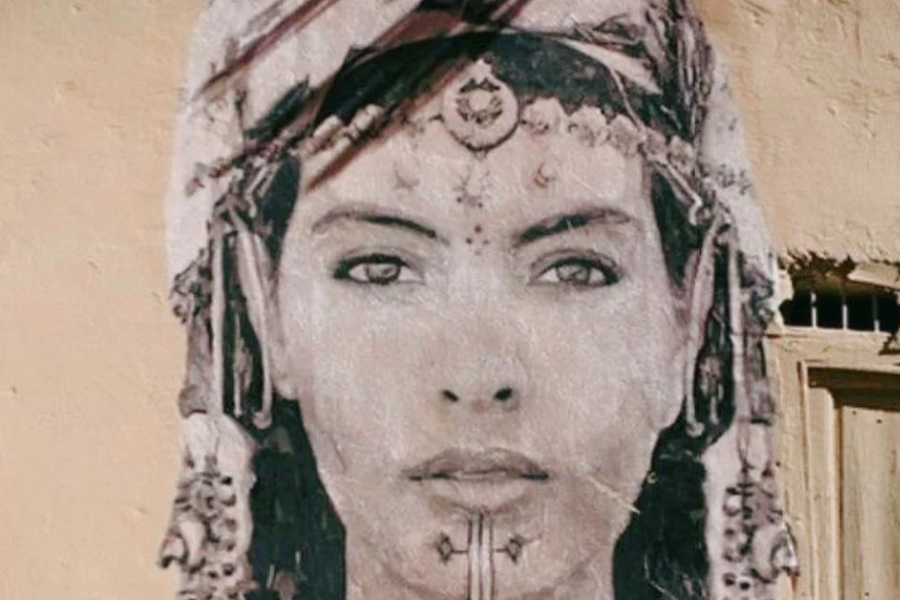

Exploring the rich tapestry of Amaziğ artistic expression unveils a world of intricate designs and vibrant symbolism, reflecting the diverse heritage and enduring spirit of the community.
Tattoos and Symbolism: A Window to the Soul In Amaziğ culture, tattoos, and symbolic motifs serve as more than just body adornments; they are sacred expressions of ancestral connections, spiritual beliefs, and personal narratives. Each mark etched into the skin carries layers of meaning, weaving a narrative that transcends the physical realm and delves into the depths of the soul.
Harmony of Music and Dance The rhythmic melodies and lively dances of Amaziğ culture resonate with a sense of collective identity and celebration. With every beat of the drum and sway of the hips, traditional music and dance breathe life into gatherings, infusing them with vitality, joy, and a profound connection to their cultural roots.
Honoring Artistic Legacies Throughout history, Amaziğ artists and musicians have left an indelible mark on the global cultural landscape. Their works speak volumes, echoing universal themes of love, longing, and liberation. From masterful paintings to soul-stirring melodies, these artistic pioneers continue to inspire and captivate audiences, their legacies enduring as testaments to the power of creativity and cultural expression.
In The Amazigh World, What Do Women Do?
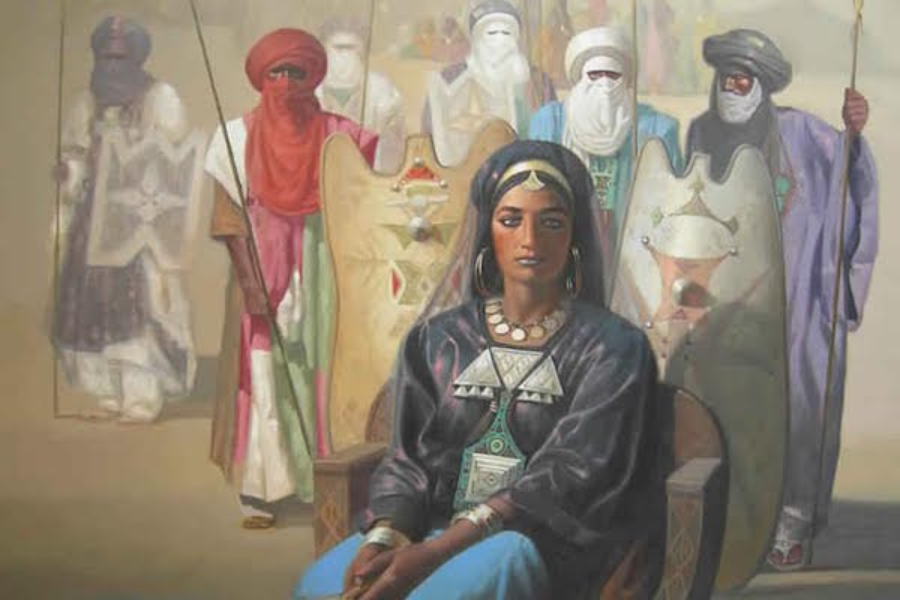

In the Amaziğ world, women play multifaceted and vital roles that are integral to the functioning of their communities. While specific duties may vary depending on cultural nuances and individual circumstances, Amaziğ women are often engaged in various tasks that contribute to the well-being and prosperity of their villages.
One significant aspect of Amaziğ women’s roles is their active involvement in agricultural activities. They participate in tasks such as planting, harvesting, and tending to livestock, playing a crucial role in ensuring food security and sustainability within their communities. Additionally, women often manage household finances and resources, overseeing budgeting and procurement to meet the needs of their families.
Beyond domestic and agricultural responsibilities, Amaziğ women also contribute to community decision-making and governance. They participate in local councils and assemblies, offering insights and perspectives that shape policies and initiatives aimed at improving village life. Moreover, women often serve as educators and mentors, passing down traditional knowledge and skills to younger generations, thereby preserving cultural heritage and fostering community cohesion.
Overall, Amaziğ women are dynamic and empowered individuals who actively contribute to the social, economic, and cultural fabric of their villages. Their roles are characterized by resilience, resourcefulness, and a deep commitment to the well-being of their families and communities.
The Islamic Conquest: Shaping North African Societies
In the 7th century AD, the sweep of Arab Muslim armies across North Africa heralded a significant turning point in the region’s history. This conquest not only brought Islam to the locale but also catalyzed a fusion of Arab culture with the rich tapestry of Amaziğ traditions. The result is a unique blend that continues to shape the cultural landscape of modern-day North African societies.
The Impact of Arab-Islamic Influence The arrival of Islam in North Africa marked a profound transformation, influencing every facet of societal life. From governance and law to language, art, and architecture, the Arab-Islamic influence left an indelible imprint on the region. Yet, this cultural exchange was not unidirectional. Instead, it sparked a dynamic interplay between Arab and Amaziğ traditions, giving rise to a hybrid identity that is distinctly North African.
A Legacy of Diversity and Resilience The legacy of the Islamic conquest is one of diversity and resilience. It is a testament to the capacity of societies to adapt and evolve in the face of change. Today, the cultural mosaic of North Africa bears witness to this enduring legacy, where Arab-Islamic influences intertwine with the ancient heritage of the Amaziğ people, creating a vibrant tapestry that reflects the rich complexity of the region’s history.
Amaziğ People Today
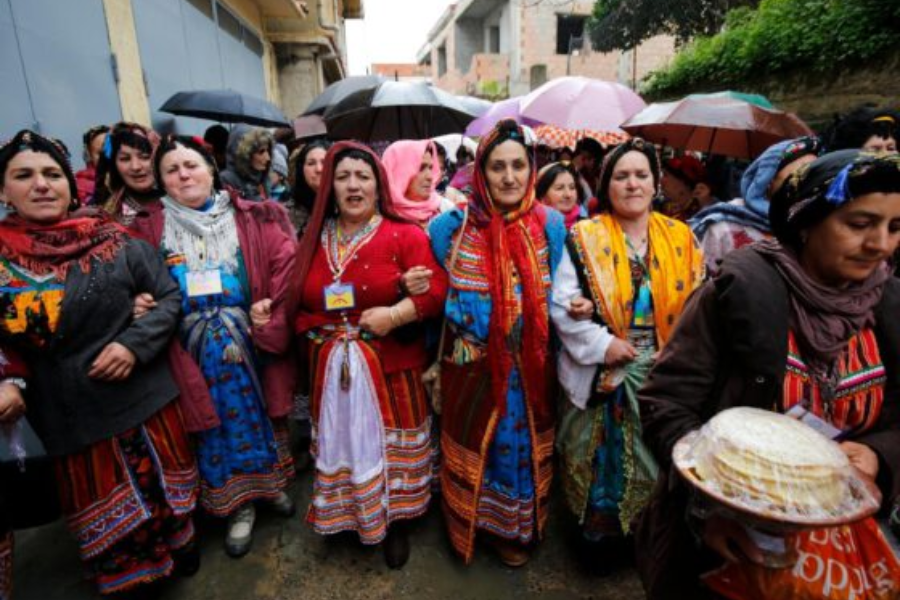

In today’s North Africa, the Amaziğ people represent a significant portion, estimated to be around 20–25% of the population, predominantly residing in Morocco and Algeria. Despite their sizable presence, they confront persistent challenges like discrimination and economic marginalization. Nonetheless, their unwavering commitment to preserving their distinct identity and cultural legacy remains steadfast amidst these obstacles.
The narrative of the Amaziğ community echoes a story of resilience and adaptation, forged through centuries of navigating external influences. Despite the pressures of history, they have managed to safeguard their cultural heritage, maintaining a vital role in shaping the multifaceted landscape of North Africa. Their enduring commitment to tradition and values serves as a beacon of strength, allowing them to assert their unique place in the region’s rich tapestry of history and contemporary dynamics.
As guardians of their cultural legacy, the Amaziğ people continue to navigate the complexities of modernity while honoring the wisdom of their ancestors. Their journey reflects a profound resilience and determination to uphold their identity in the face of ongoing challenges, embodying a living testament to the power of cultural preservation and collective strength.
Preservation Of Amaziğ Heritage And Global Unity

The Amaziğ Culture: A Living Legacy The Amaziğ culture is not merely a relic of the past but a vibrant and dynamic force shaping our collective future. Understanding and appreciating the cultural significance of the Amaziğ people not only preserves their heritage but also fosters a sense of interconnectedness and empathy within our global community.
Promoting Understanding and Solidarity Amidst a world often divided by differences, the Amaziğ culture serves as a bridge promoting understanding and solidarity. Their rich cultural heritage teaches us to celebrate and embrace diversity, offering inspiration to those dedicated to building a future of harmony and resilience.
Embracing Diversity for a Better Tomorrow As we navigate an increasingly interconnected world, the enduring legacy of the Amaziğ people reminds us of the importance of embracing diversity. By honoring their cultural heritage, we pave the way for a future built on mutual understanding, cooperation, and shared humanity.
Summary
The Amaziğ people, also known as the Berbers, are an indigenous group with deep roots in North Africa. Their history dates back thousands of years, and they are believed to be the original inhabitants of the region. Despite enduring various challenges such as cultural assimilation and marginalization, the Amaziğ community remains resilient in preserving their unique identity and heritage.
Their language, Tamaziğt or Berber, is a vital part of their cultural identity, with diverse dialects spoken across different regions. Amaziğ culture encompasses a rich tapestry of traditions, including art, music, cuisine, and religious practices. Their societal structure emphasizes strong family and community bonds, while gender roles evolve amidst changing cultural paradigms.
The Amaziğ people have made significant contributions to North African society and beyond, particularly in the realms of art, literature, sustainable living practices, and global engagement. Despite historical influences such as the Islamic conquest and Arabization, the Amaziğ culture continues to thrive, embodying resilience, diversity, and a steadfast commitment to preserving their heritage for future generations.
People Also Ask (FAQs)
1. What religion does the Amazigh follow?
The majority of Amazigh populations are Muslim, although some also practiced Christianity or Judaism historically, and a few still do in the North African region. Despite embracing Islam, many Amazigh individuals retain elements of their earlier tribal religious traditions, integrating them into their Islamic beliefs.
2. Are Algerians considered Arab?
Ethnic groups in Algeria primarily consist of Arabs and Berbers, with Arabs making up 75–85% of the population and Berbers around 15–25%. Additionally, Algeria has a minority population of Europeans, comprising less than 1% of the total population.
3. Is Berber similar to Arabic?
Berber languages exhibit a significant influence from Arabic, along with other languages. For instance, Arabic loanwords account for 35% to 46% of the total vocabulary in the Kabyle language and 51.7% in Tarifit, illustrating the linguistic interplay between Berber and Arabic.
4. What does the term “Berber” mean?
The term “Berber” refers to various peoples residing in northern Africa west of Tripoli. It also denotes a branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, encompassing languages spoken by different groups in northern Africa and the Sahara, such as the Tuaregs and the Kabyles.













+ There are no comments
Add yours